Main topic: PHARMACY COMPOUNDING: TASKS, PROBLEMS, SOLUTIONS
The matter of restoring the system of compounding pharmacies is actively discussed by members of the medical and pharmaceutical communities as well as government officials at various levels. This interview presents the views of Ayrat Z. Farrakhov, Head of the Working Group for the Restoration of Compounding Pharmacies of the State Duma Committee on Health Protection, representative to the 8th State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, member of the State Duma Committee on Budget and Taxes, Vice-President of the National Medical Chamber Medical Community Union, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, and Honoured Doctor of the Republic of Tatarstan.
INTRODUCTION. The organisation of extemporaneous compounding in pharmacies is currently considered to be a priority for the national healthcare system. Extemporaneous medicinal products used by patients should meet high quality, safety, and efficacy standards. Provision of consistent and science-based requirements for the quality of medicines, particularly those compounded in pharmacies, is a key area of concern for standardisation.
AIM. This study aimed to analyse international experience and determine areas for the improvement of standardisation approaches of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation to the quality of medicinal products compounded in pharmacies.
DISCUSSION. The study investigated the common and distinctive properties of extemporaneous preparations compounded in pharmacies (and not subject to registration) and medicinal products manufactured by pharmaceutical companies. The authors analysed the requirements and recommendations for compounding and quality assurance of extemporaneous medicinal products provided by the regulatory and pharmacopoeial authorities of the Russian Federation, the Republic of Belarus, the European Union, the United Kingdom, the USA, and Canada. The United States Pharmacopeia includes circa 150 individual monographs for non-sterile compounded drug products with particular compositions and over 20 individual monographs for sterile compounded drug products. The European Pharmacopoeia requires that extemporaneous preparation should be organised within the quality assurance framework of a pharmacy after a proper risk assessment. In the Republic of Belarus, extemporaneous medicinal products are compounded in line with the requirements of the Good Compounding Practices and the State Pharmacopoeia of the Republic of Belarus, which provide rapid testing procedures for extemporaneous medicinal products.
CONCLUSIONS. The study identified the following areas for the development of requirements for the quality of medicinal products compounded in pharmacies: the determination of rapid testing approaches; the development of pharmacopoeial monographs for active pharmaceutical substances used in extemporaneous compounding, with the Identification section supplemented with an additional subsection on pharmacy-specific analytical procedures; and the development of pharmacopoeial monographs for frequently used compounding formulae.
INTRODUCTION. National pharmacy compounding is a priority for providing the population with medicinal products, particularly the medicinal products lacking in the Russian Federation. Investigating opportunities to improve the operation of compounding pharmacies in the Russian Federation remains essential, especially in the context of the developing personalised approach to treatment, growing practice of orphan drug development, and import substitution needs.
AIM. This study aimed to identify the factors driving the development of compounding pharmacies under the current conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study focused on the Russian regulatory framework for pharmacy compounding, as well as the range of dosage forms and administration routes of the medicinal products that had been produced and packaged by the compounding pharmacies in Irkutsk in 2021–2023.
RESULTS. This study showed a demand for compounded medicinal products among both healthcare providers and patients. These medicinal products covered a traditional range of compounded medicines, including custom formulae, medicines for paediatrics and geriatrics, stock preparations, and pharmacy-packaged items. In 2021–2023, the mean annual production of Irkutsk pharmacy organisations amounted to ~500,000 units of compounded medicinal products, with a variety of doses and dosage forms. The medicinal products were compounded using ~100 different active substances and over 20 approved medicinal products. This study examined the evolution of Russian pharmacy compounding legislation. The key aspects included the establishment of a pharmaceutical quality system for compounded medicinal products, the extension of shelf life for specific dosage forms, and the authorisation to use medicinal products approved in the Eurasian Economic Union in compounding. The study showed that the main factors driving the operation of compounding pharmacies were the ongoing regulatory framework transformation and the transition from standardised treatment to personalised medicine. The main impediments for compounding pharmacies included the lack of state support, the ban on compounding medicinal products produced by pharmaceutical companies, the shortage of skilled staff, the inadequate supply of equipment (first of all, production machinery), the poor availability of active substances and excipients in small packages, and the challenges associated with regulatory control and oversight over the quality of compounded medicinal products.
CONCLUSIONS. Further stimulation of the active development of compounding pharmacies requires further investigation into their operation in other regions, which will help to develop legal arrangements for the federal and regional state support of compounding pharmacies, procure up-to-date materials and equipment, and train the staff for compounding pharmacies.
INTRODUCTION. The range of liquid multivitamins for toddlers approved in the Russian Federation comprises two imported syrups. Pharmacy compounding of vitamin syrups will meet the demand for optimally formulated multivitamins in the pharmaceutical market. Therefore, a necessary step for their release into medical practice is to develop and validate analytical procedures for assessing the quality of such medicinal products.
AIM. This study aimed to select and adapt analytical procedures for assessing the quality of a compounded multivitamin product for children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study focused on a compounded sorbitol syrup containing vitamins C, PP, B1, B2, and B6. The quantities of vitamin components in the syrup corresponded to the recommended daily intake for children aged 1–3 years. For identification, the authors used qualitative reactions and spectrophotometry. Indicator-free direct iodometry was selected for the quantitative determination of ascorbic acid. Alkalimetry with bromothymol blue was used to quantitate nicotinic acid in the presence of ascorbic acid, pyridoxine hydrochloride, and thiamine hydrochloride. The sum of thiamine hydrochloride and pyridoxine hydrochloride was determined by direct argentometry (Fajans method) with bromophenol blue in an acetic acid medium. Riboflavin quantification involved visible spectrophotometry at 445 nm and spectrofluorometry. The sorbitol content was measured by refractometry, and the calculations accounted for the content of other syrup components. The validation was conducted in line with the applicable pharmacopoeial requirements (State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation).
RESULTS. The authors selected analytical procedures for the quality evaluation of the multivitamin syrup containing five water-soluble vitamins (С, РР, В1, В2, В6) and sorbitol. These analytical procedures were adapted to the simultaneous presence of riboflavin, ascorbic acid, nicotinic acid, thiamine hydrochloride, and pyridoxine hydrochloride. The authors developed analytical procedures for the determination of riboflavin by spectrofluorometry and spectrophotometry and for the selective determination of thiamine hydrochloride by photometry after a precipitation reaction with Reinecke’s salt. The analytical procedure for the determination of riboflavin by spectrofluorometry was validated for specificity, accuracy, linearity, precision (repeatability and intermediate precision), and range.
CONCLUSIONS. The study confirmed the applicability of the analytical procedures that were selected and adapted for all components of the multivitamin syrup. The authors identified the conditions for the selective determination of thiamine hydrochloride by spectrophotometry after a precipitation reaction with Reinecke’s salt. The analytical procedure for the quantitative determination of riboflavin by spectrofluorometry was validated and considered suitable for use in analytical laboratories for the quantitative determination of riboflavin in multivitamin mixtures and for syrup stability testing.
INTRODUCTION. Currently, stakeholders across the Russian medical and pharmaceutical community are focusing on the restoration of national pharmaceutical compounding. The Russian pharmaceutical compounding market, with its great potential for growth, requires highly qualified professionals able to ensure the operation of compounding pharmacies and the proper quality of extemporaneous medicinal products. The effectiveness of training for such specialists can be improved by analysing the experience of educational institutions in countries with developed pharmaceutical compounding systems.
AIM. This study aimed to analyse the distinguishing features of training for pharmaceutical compounding specialists, as well as determine the main trends in pharmaceutical compounding education in leading international academic institutions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study used methods of logical, comparative, structural, and content analysis. The analysis covered 106 pharmacy and pharmacology curricula of the top-25 higher education providers from the QS World University Rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds. The curricula were analysed using open data published online, particularly, on the official websites of the selected universities.
RESULTS. The article presents the distinguishing features of pharmaceutical compounding education at different academic qualification levels; these features include the requirements for applicants, time to degree, competence standards, structure of exams, and specifics of students’ professional engagement, with consideration of the national context. The key trends in the education of specialists in pharmaceutical compounding include a decrease in training time for mid-level specialists; a tendency towards concentrating on clinical disciplines due to the expansion of the roles of pharmacy professionals; a growing focus on specialisation in the areas of paediatric, dental, sterile, veterinary, radiopharmaceutical, and orphan drug compounding; increasing use of simulated practice experiences and online learning technologies; and the development of continuing professional education systems.
CONCLUSIONS. Pharmaceutical education programmes of leading international educational organisations include disciplines related to extemporaneous compounding. Current international trends—pharmaceutical education with further specialisation in extemporaneous compounding, integration of simulation technologies and online learning into the educational process, and development of continuing professional education—coincide with the development directions of pharmaceutical education in the Russian Federation. Whereas international pharmacy specialists complete additional professional education programmes to gain an additional specialisation in the extemporaneous preparation of paediatric medicinal products, sterile dosage forms, chemotherapy products, radiopharmaceuticals, veterinary products, and dental products, Russian specialists can acquire these additional competencies through further education programmes at the levels of advanced training and residency.
INTRODUCTION. Pharmacy compounding involves certain risks that are directly related to the process of extemporaneous preparation and the actions of its participants. However, the role of pharmacy cleaners, whose actions can influence the quality of compounded medicinal products, has not been studied yet.
AIM. This study aimed to analyse the risks to the quality of compounded medicinal products associated with the functions of a pharmacy cleaner in pharmaceutical compounding of non-sterile dosage forms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study used failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) in accordance with the relevant Russian State Standard, as well as open brainstorming discussion. The study examined the functions of a pharmacy cleaner in pharmaceutical compounding of non-sterile dosage forms. The results were assessed by statistically processing the study data and assigning each potential failure mode a certain category.
RESULTS. The risk analysis identified 45 potential failure modes for the functions of a pharmacy cleaner. Of these, 12 failure modes (26.7%) had a high level of criticality, 14 failure modes (31.1%) had a medium level of criticality, and 19 failure modes (42.2%) had a low level of criticality. Not all potential failure modes had valid documented regulatory provisions for the risk assessment and the development of prevention-type controls.
CONCLUSIONS. The analysis of the functions of a pharmacy cleaner highlighted the potential risks to the quality of extemporaneous medicinal products prepared by compounding pharmacies. The study identified a lack of valid regulatory documentation. The authors suggested using the study results to amend the regulatory documents and standard operating procedures (SOPs) guiding the work of a pharmacy cleaner, to develop illustrative educational materials, and to conduct on-the-job training for pharmacy staff.
PRECLINICAL STUDIES
INTRODUCTION. The determination of nephrotoxicity markers is a useful and necessary step in the detection of renal injury in animal experiments; these markers help accurately localise organ damage. With multiple damaging agents, known nephrotoxicity mechanisms, and laboratory animal species, there is currently no widely accepted renal injury marker that meets all the prerequisites.
AIM. This study aimed to collate literature data on nephrotoxicity markers, evaluate their prognostic significance, and formulate general recommendations for assessing urinary system function in preclinical studies.
DISCUSSION. This article describes a comparative analysis of the nephrotoxicity markers recommended by regulatory authorities for monitoring drug-induced kidney injury. According to the results, the most commonly used and prognostically significant markers of acute kidney injury in preclinical studies are cystatin C, albumin, total protein, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-2 (NGAL), and clusterin. Chronic kidney injury markers include the above, plus the glomerular filtration rate, creatinine, urea, and osteopontin. An electrolyte panel can be used for the differential diagnosis of pre-renal azotaemia and acute kidney injury. Potential limitations for the routine use of kidney injury markers in preclinical research include the high cost of their quantitative determination and the lack of information on the applicability of data obtained from different species of laboratory animals.
CONCLUSIONS. Having compared the prognostic significance of common biomarkers, the authors provided general recommendations for a comprehensive preclinical assessment of urinary system function, including laboratory investigations, instrument-based tests, and necropsy. A preclinical study design should be based on the study aims, the species and number of animals used, and special considerations for the test article.
CLINICAL STUDIES
INTRODUCTION. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic functional disorder present in over 13% of the population. Despite the wide prevalence of IBS, there is currently a lack of well characterised authorised medicinal products to treat IBS. This situation stems from both poor engagement in the development of such medicinal products and the absence of sound approaches to their regulatory review. The intensification of drug development aimed at improving the safety and efficacy of IBS therapy in the context of the growing common pharmaceutical market of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) requires guidelines for planning and conducting clinical trials of medicinal products for IBS.
AIM. This study aimed to evaluate the possibility of using the methodological approaches described in international guidelines for the development of national recommendations for conducting clinical trials of medicinal products for IBS.
DISCUSSION. The authors analysed the main provisions of the Guideline on the evaluation of medicinal products for the treatment of IBS by the European Medicines Agency (EMA). The analysis identified the methodological tools, the scope and stages of clinical trials, and the efficacy criteria for each study stage. The authors assessed the specific aspects of diagnosing IBS, which are considered when determining the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. This review highlighted the need for the harmonisation of national and international methodological approaches to the evaluation of clinical trial results that would ensure more robust results of clinical trial reviews conducted in different countries. The authors determined the considerations for planning exploratory and confirmatory clinical trials, including the selection of endpoints, design, and duration of clinical trials in adults and children, as well as the sex distribution of the trial population.
CONCLUSIONS. The EMA’s recommendations may guide the planning of clinical programmes for novel medicinal products for IBS. These recommendations may be applied by experts reviewing clinical trial results, as well as developers creating new medicinal products.
QUALITY CONTROL OF MEDICINES
INTRODUCTION. The metrological characterisation of analytical procedures helps in selecting a procedure that will provide reliable and consistent results. This is particularly relevant in cases where a pharmacopoeial standard includes several test methods for a quality parameter of a medicinal product. For example, the water content of a lyophilisate can be measured by volumetric or coulometric Karl Fischer titration (semi-micro and micro determination) and by the loss on drying.
AIM. This study aimed to investigate the correlation between the method selected for the determination of water content in a lyophilisate and the results obtained by this method via analysis of variance (ANOVA), as well as to evaluate the uncertainty of water content measurements by Karl Fischer titration.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study focused on a lyophilised micafungin medicinal product. The water content in the lyophilisate samples was measured by Karl Fischer titration (semi-micro and micro determination) and, additionally, by the loss on drying as outlined in the Pharmacopoeia of the Eurasian Economic Union (General Monograph 2.5.1.14 Lyophilisates). The authors performed ANOVA using Microsoft Excel to assess the effect of the test method on the results. The authors conducted statistical analysis of the experimental results, including Fisher's test to assess the reproducibility and Student's test to compare the mean results obtained by two different methods. To assess measurement uncertainty, the authors calculated confidence interval limits at confidence levels of 0.95 and 0.99.
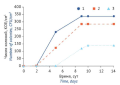
RESULTS. ANOVA demonstrated that the method selected to determine the lyophilisate water content had an effect on the results obtained. Karl Fischer titration (semi-micro and micro determination) provided reproducible results; the F-values calculated for four lyophilisate batches (F1=2.3440, F2=1.0762, F3=3.5302, and F4=1.0989) were lower than the critical F-value (Fcrit(0.95;2;2)=19.000). The mean results of different methods were statistically dissimilar; the calculated t-values (t1=9.2391, t2=11.4847, t3=11.0041, and t4=33.6502) exceeded the critical t-value (tcrit(0.95;2)=4.3027). To assess the measurement uncertainty, the authors calculated two-sided confidence interval limits using Student's test at confidence levels of 0.95 and 0.99. The measurement uncertainty of the semi-micro method was lower than that of the micro method.
CONCLUSIONS. The results of water determination in the micafungin lyophilisate depend on the method used. Micafungin water content is not commonly quantified by the loss on drying, and the methods of semi-micro and micro determination are not interchangeable for this purpose. Further studies are required to estimate bias and include the estimate in the measurement uncertainty budget.
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING
INTRODUCTION. Microbiological environmental monitoring programmes for clean rooms for pharmaceutical production vary depending on the regulatory document. This is particularly evident in the experimental conditions, including the culture media used for sampling, as well as the temperature and time of incubation. To harmonise quality control procedures, it is necessary to develop a unified strategy for processing microbiological samples.
AIM. This study aimed to investigate the optimal conditions for sample incubation during microbiological monitoring of clean rooms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study compared several culture conditions for indicator microorganisms, including Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, Candida albicans ATCC 10231, Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404, Aspergillus fumigatus F-62, Aspergillus terreus F-1269, and Penicillium chrysogenum F-3 (the latter three strains were obtained from the Russian National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms), as well as for environmental isolates, including Staphylococcus epidermidis, Kocuria rosea, Micrococcus luteus, Bacillus spp., and Sphingomonas paucimobilis. The culture media used were trypticase soy agar (TSA), Sabouraud's dextrose chloramphenicol agar (SDCA), and Reasoner’s 2A agar (R2A). The incubation regimes used were as follows: 2 days at 30–35 ºC and then 3 days at 20–25 ºC; 3 days at 20–25 ºC and then 2 days at 30–35 ºC; 48–72 hours at 30–35 ºC (for aerobic bacteria); 5–7 days at 20–25 ºC (for yeasts and moulds).
RESULTS. The comparison showed no statistically significant differences between the results obtained with TSA and R2A under different temperature
conditions. The germination rates of environmental isolates grown on TSA were significantly lower (by 19–37%) in the two-tiered incubation scheme that started at a lower temperature. The study identified groups of microorganisms requiring special culture conditions for microbiological environmental monitoring (bacteria with suppressed physiological functions and moulds).
CONCLUSIONS. The study confirmed the need to standardise microbiological testing used in environmental monitoring and to provide for its proper regulation by drafting a general monograph on the matter. The authors demonstrated the applicability of both TSA and R2A as culture media for microbiological environmental monitoring. Currently, the use of a two-tiered incubation scheme with one non-selective culture medium requires validation on a case-by-case basis. Although the sequence of temperature levels did not affect the germination rates of microorganisms significantly, the incubation regime starting at a higher temperature (30–35 ºС) was determined as preferable for bacterial environmental isolates.
ISSN 3034-3453 (Online)